Why talk about SOC 2 for Startups?
SOC 2 for Startups is no more a nice-to-have but a necessity amidst the growing Data Security concerns. Data Breach and declining Digital Trust are major issues for the companies across the globe.
The problem is especially critical for the US tech industry. On an average, the cost per Data Breach for a US-based company is USD 9.44 million, (more than twice the global average!). Bigger organizations are coping with the problem by transferring the costs to the customers, however, this is not possible for SMBs.
For tech Startups and SaaS companies, preventing Data Breach is a much more serious and fundamental concern. Occupying the lower rung has its disadvantages and making up for additional costs by charging more is not an option. That’s where SOC 2 for startups becomes crucial.
Organizations want to place their trust in Startups that inspire confidence in matters of data security, privacy, and protection.
Without the big-ticket clients that can bring higher profit margins, up-scaling is impossible.
Digital Trust based on cybersecurity, data privacy, and responsible AI can translate into a 10% annual growth.
Keeping all the bases covered in matters of data security and compliance is the best policy ahead. SOC 2 for startups serves precisely this purpose, especially if they are working on SaaS models or relying on Cloud.
What is SOC 2 for Startups? And, what it is not!
Service Organization Controls 2 or SOC 2 is an all-encompassing compliance, auditing, and reporting framework governed by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA). The responsibility of updating and maintaining the SOC 2 lies with the Certified Public Accountants (CPAs).
An SOC 2 audit conducted by third-party auditors results in an Attestation Report. An organization shows the Attestation Report to prove its SOC 2 compliance to interested customers.
Why was SOC 2 created?
The chief aim behind laying the SOC 2 framework was to ensure secure storage, processing, and usage of client data by third-party service providers.
As a compliance framework, SOC 2 was created for software vendors and tech companies with customer data. It enables them to demonstrate the security controls in place to protect the data of their customers.
Being an auditing framework, SOC 2 is for independent third-party auditing by certified accounting firms and agencies. It provides the outline and standards for auditing, assessing, and verifying the security processes and controls employed for protecting and managing data.
The many meanings of SOC 2
SOC 2 is a generic term which carries various interrelated meanings, though with subtle differences. Officially, and for the AICPA, SOC 2 is a Reporting Framework.
For CPAs, accounting firms, and independent auditors or agencies, it’s an Auditing Framework.
SOC 2 is a Compliance Framework for SaaS companies and tech Startups.
SOC 2 acts as a Security Standard or a Compliance Standard. Sometimes, it is an ‘Audit’. Loosely (and inaccurately!), it’s a certification!

SOC 2 for Startups vs. Large Organizations – What’s the difference?
SOC 2 carries a different weight and significance for Startups. For larger organizations, SOC 2 may be a routine since they may be already complying with it. Their level of familiarity and past data security efforts contribute to their staying SOC 2 compliant.
For Startups, SOC 2 poses challenges.
Startups are often confused about the nature of SOC 2. They have difficulty understanding its overall framework, requirements, and the process of compliance. Many new companies cannot appreciate its benefits, or that SOC 2 compliance takes time. Months!
SOC 2 for startups is a necessity in today’s Data Security conscious environment. Despite its complexities, the detailed paperwork it demands, and the costs involved, SOC 2 is crucial for promising Startups. They may choose to ignore or delay it at their own risk!
What SOC 2 is not?
SOC 2 is absolutely not a certification.
The SOC 2 audit results in a comprehensive report. This attestation report carries the opinion of the auditor regarding the operating effectiveness and design of controls. SOC 2 is absolutely not a security certification! Unlike the HIPAA compliance certification, you don’t pass or fail the SOC 2.
SOC 2 Compliance is not a legal requirement.
SOC 2 is voluntary, not mandatory! Startups should begin their journey towards SOC 2 for the benefits it offers, and not under any external pressure.
SOC 2 is not a substitute for Security Best Practices.
Startups choose to become SOC 2 compliant to gain a competitive advantage and win the trust of prospective enterprise clients. The SOC 2 attestation reports carry the auditor’s opinion. A positive opinion does not mean that you are meeting the best security standards.
What is SOC 2 Compliance?
SOC 2 Compliance is a term used from the perspective of software vendors, tech companies, SaaS Startups, and their customers. If an organization complies with the SOC 2 requirements, it is believed to observe high standards of information security. Therefore, it is safe to do business with the complying organization.
In this sense, it’s a desired status that shows greater trust and higher confidence of prospective enterprise-level clients in the scenario of B2B dealings. SOC 2 compliance can also come as a customer request before signing a business contract. However, such a request is not feasible since SOC 2 reporting can take months.
To achieve an SOC 2 Compliant status, Startups need to undergo an auditing process, resulting in an attestation report. The SOC 2 report evaluates the organization’s own claims regarding its quality of security controls.
Who needs SOC 2 Compliance?
There are different factors that determine whether a startup needs to get an SOC 2 compliance report. Again, for the sake of avoiding confusion, let’s just recall that law or the government do not mandate SOC 2. It’s voluntary, but it is needed for SaaS Startups to build trust with mid-market and enterprise-level prospects.
The factors governing the need for SOC 2 compliance include:

Factors determining the need of SOC 2 for Startups
Stage of the Startup
Early stage Startups should not worry about SOC 2. However, if your Startup is entering the growth stage, it’s time to take SOC 2 seriously. If you are already beyond the growth stage and without a compliance report, it should be a top priority for you.
Growth and Expansion Plans
There are different ways in which your startup may scale from its growth stage. If you are looking to scale gradually, then the SOC 2 may not be a matter of urgency. However, if you are looking for a breakthrough that sets you on the path to expansion, then you should make SOC 2 a top priority. You need SOC 2 to win enterprise deals!
Your Client’s Business and Industry
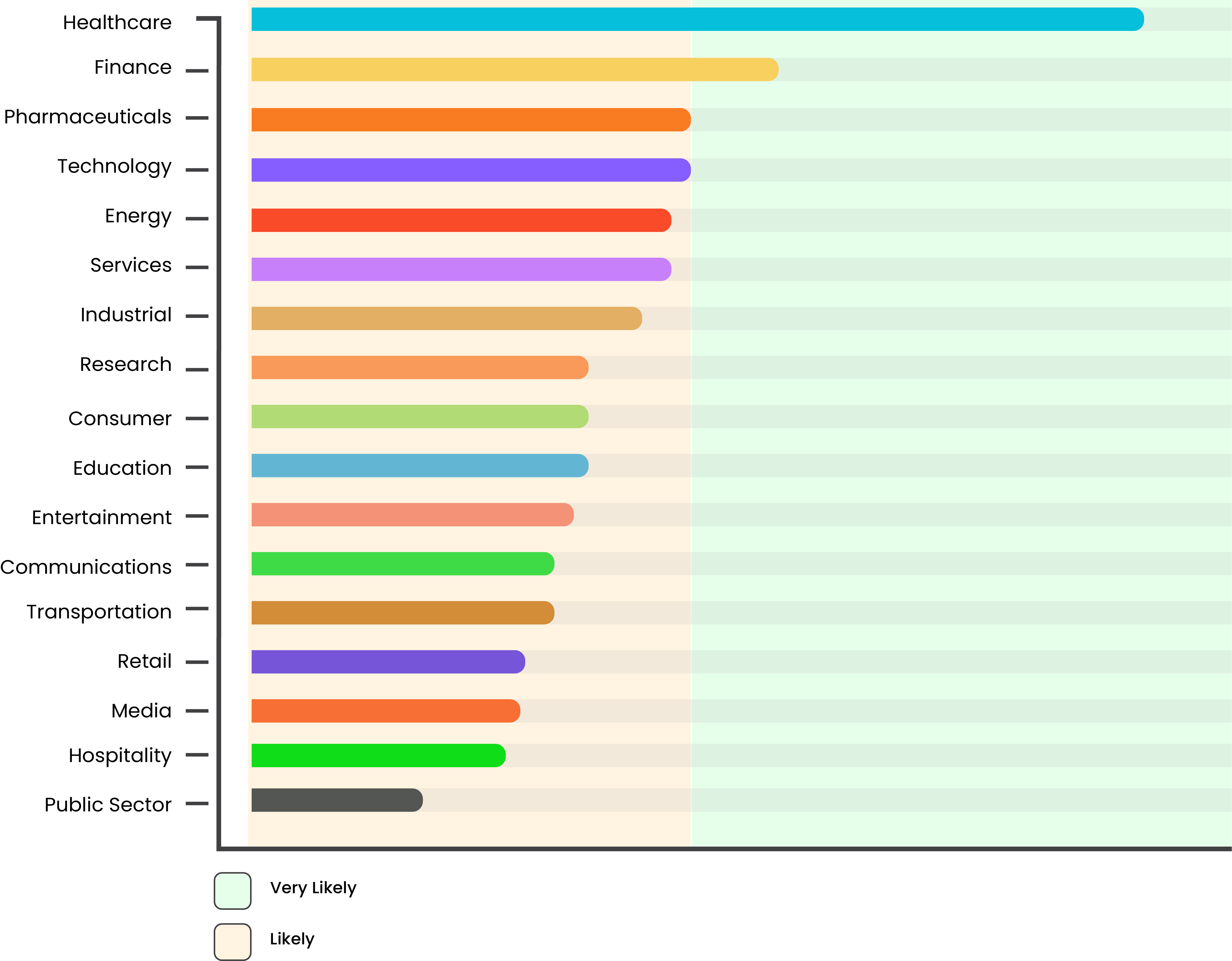
Data Breach and Digital Trust are major issues of concern in the current environment of rapid Digital Transformation. Mark the industries of the prospective enterprise clients you are aiming to do business with in the coming phase. It’s time for action if your future clients are operating in any of the following industries.
- Healthcare
- Finance
- Pharmaceuticals
- Technology
Companies operating in these industries are more likely to be cautious regarding data security standards. This is owing to the additional costs they have to bear and pass on to their customers owing to Data Breaches. Therefore, you should not delay starting the SOC 2 process for your startup if you are planning to break into any of these segments.
Your Startup’s Business and Industry
Your Startups core business and the industry it is operating in also dictate the need for compliance. This is regardless of the fact whether your model is B2B or B2C! Needless to mention that healthcare and financial data are extremely sensitive. You would lose potential clients and customers without SOC 2.
However, you may need an SOC 2 owing to the underlying operational processes of your business. SOC 2 is critical if your startup is offering e-commerce services. If you have to depend upon, or work with, Big Data, your clients and customers will request your SOC 2 report.
Importance of SOC 2 for Startups
There are reasons beyond trust-building and up-scaling to prioritize SOC 2 compliance for startup. A proactive approach towards attaining SOC 2 is always better than waiting for a request.
Starting and Encouraging the right Cybersecurity Culture
SOC 2 is not just about a positive market perception of your startup. It’s also about laying the groundwork of a security-first culture within your company. You may choose to attain the SOC 2 attestation report before trying to expand by onboarding enterprise clients.
It’s better to aim for compliance at the early-stage itself. SOC 2 controls operate within an organization day in and day out. When your startup has to operate with high data security standards, it becomes a work-culture less painfully.
Your employees and teams don’t need to make adjustments if your startup is SOC 2 compliant after the first year. DevOps personnel code with security vulnerabilities in mind. Everyone at the company opens emails carefully. Sensitivity to customer data and alertness against hackers and unwanted access becomes a habit. It is easier to identify vulnerable systems, processes, and personnel within your organization.
Organizations that choose to be SOC 2 compliant from the outset are easier to manage and scale. Their employees live and breathe a security-first culture, which they pass and propagate. As the teams expand and your startup works on bigger projects, cybersecurity becomes a way of living, not a burden.
Your startup can also save significant architecture redesigning costs by building a strong data security foundation from the outset with SOC 2.
Building Stakeholder Confidence
Startups need new investors. By attaining SOC 2, you become more attractive to venture capitalists. Data Breach is a major issue for tech investors. Startups with SOC 2 are good for investment. SOC 2 compliance proves better market reputation, lower risk, and higher chances of expansion by gaining enterprise-level customers.
Streamlining Internal Processes
The SOC 2 framework has a very broad scope. The prerequisites for SOC 2 audit go beyond cybersecurity. For example, while preparing for the SOC 2 audit, you will need to establish several entity-level controls for security. These controls include HR procedures for employee onboarding and onboarding, documentation, performance reviews, security risk assessments, security training, etc. On their own, these controls and processes may not be necessary for a startup. However, they are crucial during the expansion phase.
The pre-auditing SOC 2 process prepares you for the future by setting and streamlining. These processes go ignored until startups reach the expansion stage. At this later stage, when Startups are working on tougher and bigger projects, the setting up of these processes disturbs the workflow.
An SOC 2 process from the outset helps you streamline various internal processes while creating the path for smooth scalability. Early stage SOC 2 compliant Startups have high rates of customer retention, higher employee productivity, and few data breach incidents.
Saving Time, Reducing Disruption, Contributing to Business Growth
SOC 2 involves an intensive process for which you will have to designate personnel in your organization. Delaying SOC 2 until your customer demands a report is therefore not a good idea. It will disrupt the workflow and consume your organization’s precious time.
By getting the SOC 2 report on a prospective customer’s request, you won’t be able to establish a security-first culture. In fact, you may end up hurting your employee’s confidence and damage their attitude towards data security.
Prior SOC 2 compliance saves time! It will allow you extra time to devote to your core business, when it will matter the most – the expansion stage. Your scaling-up will be smooth and free of disruption.
SOC 2 reports lead to faster sales cycles by being a single substitute for many RFIs required for each sale.
SOC 2 can do more than save time and prevent disruptions at crucial junctures on your startup’s journey. It can help you win more and bigger customers, propelling your startup’s exponential growth.
Mitigating Data Breach risks
Data Breaches can prove costly for your startup. Besides, a serious data breach can strike a blow to your reputation, and that’s the last thing you would want as a startup.
SOC 2 does not guarantee a 100% protection against data breaches. However, strong controls for data protection and cybersecurity ensure data breaches are avoided and minimized. They act as a safeguard against the hackers. SOC 2 controls also offer protection against internal lapses, such as system failures, accidental data leaks, and technical misconfigurations, etc.
Avoiding Data Security Lapses
Once you set the cybersecurity culture in your organization with the first SOC 2 report, you would want to maintain your status. Your Startup will earn a reputation and perform better after the first SOC 2 audit report. Also, your teams will feel more confident and comfortable with strong data security controls in place.
SOC 2 controls promote multi-factor authentication, encryption on transmitting and stored data, firewalls, and data backups, etc. With strong data security mechanisms in place, your startup will always be on its toes to tackle information security breaches. That’s a good habit! Annual SOC 2 reports plug all data security gaps, and keep your employees and customers assured of data security.
Gaining a Competitive Advantage
SOC 2 compliant SaaS Startups not only enjoy a better reputation, but they close more deals, too. If you are an early-stage startup, then SOC 2 may not be a matter of urgency for you. However, an SOC 2 report lets your startup stand out from the crowd. It may provide that hidden force that you will need to beat your competitors. It tells your potential customers that you take data security seriously, encouraging them to do business with you.
Many startups survive and do satisfactory business without compliance. However, they stagnate due to declining customer retention. The problem is not their quality of products and services. Instead, the growing concerns for data security discourage their customers. Even the happy ones!
Startups without SOC 2 are unlikely to do business with enterprise clients. It becomes a major roadblock to their growth. Mid-market and enterprise clients are very particular about the data protection controls. They are unlikely to do business with your Startup unless the data security standards of your organization satisfy them. Over 40% of the companies are already submitting a proof of cybersecurity along with their proposals as an essential requirement. The figure will rise further in the coming years owing to supply chain attacks.
An SOC 2 report tells enterprises you are a reliable company in data handling matters. They will choose you over Startups without an SOC 2 report. By reducing due diligence time, prior SOC 2 reports will make your company a preferred choice.
Building and Maintaining Credibility
It’s not an exaggeration to say that we are living amidst a Digital Trust crisis. Enterprises are spending more time, money, and resources in ascertaining the data security controls before entering into deals with emerging companies.
SOC 2 compliance report is a mark of credibility both for your prospective customers and your investors. It’s a proof of your sincerity towards data security throughout your operations. It acts as an inexhaustible source of stakeholder confidence.
Understanding the SOC 2 Framework
In order to attain SOC 2 for startup, you will need a thorough understanding of the framework before beginning the SOC 2 process.
Trust Service Categories (TSCs) are the main component of SOC 2 framework and sit at the top of the hierarchy. You will need to define, set up, and implement Information Security Controls depending upon the TSCs you choose.
AICPA outlines its approach for companies to begin the SOC 2 process through a few points. These points help companies implement controls based on TSCs.

Information Security
Information Security is the central concern of SOC 2. It relates to protecting data of clients and customers from unauthorized access and use.
Secure Logical and Physical Access
Securing Logical and Physical Access is about restricting access to data, devices, and networks. They help in identifying authorized personnel to manage access while also laying out the roles, responsibilities, and privileges.
Continuous System Operations
System Operations relates to the strength and efficiency of the infrastructure to detect and tackle deviations and disruptions in operations. It also focuses on the time required for mitigating the process deviations to avoid information security breaches.
Change Management
Change Management refers to secure handling of infrastructure, software, processes, or data after the updates. Preventing unauthorized changes during the updates is a central concern here.
Risk Mitigation
Risk Mitigation is meant to encourage identification, tracking, and monitoring of risks to business and services. These risks may relate to information security, location, or growth.
What are SOC 2 Trust Service Categories (TSCs)?
There are five categories for controls related to the storage and management of client data. ‘Security’, ‘Availability’, ‘Processing Integrity’, ‘Confidentiality’, and ‘Privacy’ are the five TSCs defining the overall scope of the SOC 2 framework. While ‘Security’ is a mandatory category for SOC 2 compliance, the remaining four are optional.
Security
‘Security’ is mandatory and required for all SOC 2 reports. The SOC 2 audit is not complete without the Security category and underlying criteria. It determines the overarching security standards for your Startup and sets the controls for Availability, Processing Integrity, Confidentiality, and Privacy categories.
Security Category focuses on protecting information and systems from unauthorized access. It tests customers’ data and keeps it protected. It covers creation, collection, processing, transmission, storage, and usage of data and the systems that handle the data.

Five SOC 2 Trust Service Categories
Availability
The ‘Availability’ category ensures the security and availability of systems for clients and employees. Customers and clients need the availability of systems to access the services, their personal data, or to communicate. Employees need the availability of systems to perform their duties.
Network performance, server downtime, and security event handling etc. fall under ‘Availability’ category.
Though ‘Availability’ related criteria are optional, they are important for SaaS Startups and Data centers.
Processing Integrity
‘Processing Integrity’ pertains to the systems processing data for the organization. It ensures that the information processing carried out by the systems is complete, accurate, timely, and validated. Incident-free processing, storage, and maintenance of data falls under the criteria related to ‘Processing Integrity’. Therefore, it also covers the possibilities of processing errors and their diagnosis, detection, and fixing mechanisms.
‘Processing Integrity’ tells your customers that the data processes are smooth, without discrepancies, fast, and error free. It also means that the systems handling the processes are safe from unauthorized access, and the data cannot be manipulated during processing.
‘Processing Integrity’ is of critical importance to startups offering e-commerce services, payment processing services, and FinTech startups.
Confidentiality
The ‘Confidentiality’ category aims at protecting confidential information by restricting access, usage, and storage. The data covered by this criteria falling under ‘Confidentiality’ has to be designated as confidential for the customers. It may or may not be personal data. These criteria also guide the identification, protection, and destruction of confidential information.
‘Confidentiality’ confirms that your startup respects the confidentiality of sensitive information such as intellectual property, business plans, and trade secrets, etc. It demonstrates that such sensitive data is handled, allowed accessibility, and protected by high security standards.
For startups operating in the B2B space, and with prospective clients that may have customer data of confidential nature, ‘Confidentiality’ is important.
Privacy
The ‘Privacy’ category applies only to the personal information of clients and customers. Unlike ‘Confidentiality’, where information needs to be designated as confidential, the ‘Privacy’ applies by auto-identification of personal information.
Criteria falling under ‘Privacy’ tell the customers and clients that their personal information is collected, handled, and stored following high standards of data security. Such information may include name, age, contact information, email address, Social Security number, ID details, account details, and purchase history, etc.
‘Privacy’ related criteria are important for Startups operating in the e-commerce industry. Besides, it is also important for SMBs whose customers are highly conscious of the privacy of their personal data.
How to choose the SOC 2 Categories and Criteria?
Criteria falling under ‘Security’ category are mandatory to get an SOC 2 report, so there’s no choice! For the remaining four, you can consider the following questions to decide the TSCs you should opt for initially.

What is your core business?
Depending upon your core business, you can choose one or more of the optional criteria. Here are a few critical TSCs for SOC 2 for startups based on business type and industry.
Are you planning to target Enterprise-level clients?
Most Startups don’t target enterprise clients from the outset. You are most likely not an exception!
However, if you are planning to target enterprise clients in the coming months, consider ‘Confidentiality’. Enterprises lay maximum importance on security and confidentiality compliance.
Which industries are you planning to sell to?
Attitudes to Data Security vary by industry and they are often guided by the fears and costs of Data Breaches. Choose comprehensive SOC 2 reporting if you are planning to onboard enterprise clients from healthcare, financial, pharmaceuticals, or technology sectors. The average Data Breach costs in these sectors are high, which makes them extra conscious about data security compliance.
What are your prospective clients’ expectations?
There’s no alternative to researching your prospective clients’ expectations of data security. Try to find out their data security concerns. There’s no harm in asking them directly.
The ‘Processing Integrity’ and ‘Availability’ criteria take precedence if financial transactions are in the picture. In B2C scenarios, ‘Privacy Criteria’ becomes critical. Well, these are just a few hints! You’ll have to do your homework to avoid spending extra time and money on SOC 2.
Types of SOC 2 Reports
There are two types of SOC 2 reports, Type 1 and Type 2. SOC 2 for startups begins with a Type 1 report and the compliance cycle begins with the first Type 2 report.
SOC 2 Type 1 Report
The SOC 2 Type 1 report is a basic report. Its scope is limited to assessing the design of security controls at a specific point in time. To get this report, identify the controls and document the control policies. Besides, you will also need to collect evidence that the controls in place are functioning at the time of auditing.
The assessment for SOC 2 Type 1 report involves staff interviews, a walkthrough of the facility, and a thorough review of control documentation. It takes a few weeks to 3 months to get a Type 1 report.
SOC 2 Type 2 Report
The SOC 2 Type 2 report is a detailed report with a wider scope. It is based on the assessment of the functionality of controls and processes over a period. The Monitoring Period lasts from 3 to 12 months for the first SOC 2 Type 2 report. Subsequently, the Monitoring Period is 12 months, for each annual report. During the Monitoring Period, the efficacy of controls set up by the startup is rigorously assessed. The company should operate without deviation from the established controls and procedures during this period. All the policies should be followed.
The Type 2 report audit can assess the actual operational efficacy of data security controls.
To attain SOC 2 for startup, you will need an SOC 2 Type 2 report.

Understanding the SOC 2 Controls
Controls are the basis of SOC 2 evaluation and reporting. Each Control is a specific set of policies, procedures, processes, and systems focusing on a particular aspect of data security. By implementing these policies, procedures, processes, and systems, you implement a Control, to comply with a specific TSC.
As a startup, you choose the compliance categories (TSCs) and the type of SOC 2 report you want. However, for AICPA and the auditors, the SOC 2 framework is a bunch of controls.
It is important to familiarize yourself with the different categories of controls and understand how they correspond to the TSCs.
To begin with, there are two types of controls: Common Criteria (CC), and Specific Criteria. The Common Criteria correspond to the Security category, while the Specific Criteria relate to the Availability, Processing Integrity, Confidentiality, and Privacy categories.

Common Criteria Controls and Security Controls
Common Criteria (CC) Controls or Security Controls are common to all five categories of Trust Services. Remember that Security Controls overlap Controls from other categories! There are nine series of CC Controls, of which five are Essential Common Criteria Controls, and four are Additional Common Criteria Controls.
CC1 Series – Organization
CC1 Series controls relate to the organization of your startup, or the environment in which all the controls will operate. They lay the foundation of ethics and integrity over which all the other controls are established.
| Control Criteria | Objective |
|---|---|
| CC1.1 | Commitment to ethical values and integrity |
| CC1.2 | Board’s independence from the Management, and its oversight on the Management |
| CC1.3 | Establishing roles, responsibilities, and reporting structure with clarity |
| CC1.4 | Retention and development of employees that are performing well |
| CC1.5 | Building a culture of accountability around responsibilities related to internal controls |
CC2 Series – Information and Communication
CC2 Series controls relate to Information and Communication. They focus on collection and dissemination of information within and outside the organization. They strengthen the information security architecture by encouraging investigation against control violations.
| Control Criteria | Objective |
|---|---|
| CC2.1 | Use of relevant information for supporting internal controls |
| CC2.2 | Clear communication of responsibilities and objectives of controls |
| CC2.3 | Communicating with external parties regarding issue impacting internal controls |
CC3 Series – Risk Assessment
CC3 Series controls focus on financial and technical risk assessment.
| Control Criteria | Objective |
|---|---|
| CC3.1 | Specification of objectives for risk assessment enablement |
| CC3.2 | Identification and management of risks |
| CC3.3 | Consideration of a potential fraud in risk assessment |
| CC3.4 | Identification and assessment of changes that can impact internal control system |
CC4 Series – Monitoring
CC4 Series controls deal with the monitoring of adherence to controls. They lay the foundation for the auditing process, and help in outlining the strategy for communicating the audit results to stakeholders.
| Control Criteria | Objective |
|---|---|
| CC4.1 | Evaluations to ensure that all components of internal controls are functioning. |
| CC4.2 | Evaluation and communication of internal control deficiencies for timely corrective action |
CC5 Series – Control Activities
The CC5 series of controls relates to Control Activities themselves. These activities occur within and between the technology environment, policies, and procedures adopted by your startup. CC5 series controls aim at establishment of policies for Control and their dissemination to personnel.
| Control Criteria | Objective |
|---|---|
| CC5.1 | Selection and development of control activities to mitigate risks |
| CC5.2 | Selection and development of general control activities over technology |
| CC5.3 | Deployment of control activities through policies and procedures for putting policies |
There are four additional CC controls.
CC6 Series – Logical and Physical Access Controls
The Logical and Physical Access Controls are one of the most important sets of controls in the SOC 2 framework. They tie the policies, procedures and implementation of each component of the information security architecture together.
| Control Criteria | Objective |
|---|---|
| CC6.1 | Implementation of logical access security software, infrastructure, and architecture over protected data |
| CC6.2 | Authorisation of internal and external users before issuing credentials and granting access to systems |
| CC6.3 | Management of access to protected data based on roles and responsibilities |
| CC6.4 | Restricting access to physical facilities and protected information assets to authorized personnel |
| CC6.5 | Discontinuation of logical and physical protection over physical assets |
| CC6.6 | Implementation of logical access security measures for protection against external threats |
| CC6.7 | Restricting the transmission, movement, and removal of information to authorized personnel |
| CC6.8 | Implementation of controls to detect and prevent introduction of unauthorized or malicious software |
CC7 Series – Systems and Operational Controls
The Systems and Operational Controls focus on the tools for detecting vulnerabilities and anomalies in the security architecture. These controls show the speed of response against disruptions to normal operations, which is important for mitigating risks.
| Control Criteria | Objective |
|---|---|
| CC7.1 | Detection and monitoring vulnerabilities due to configuration changes and threats posed by new vulnerabilities |
| CC7.2 | Monitoring of system components and their operations to detect anomalies like malicious acts, errors, and natural disasters |
| CC7.3 | Evaluation of Security Events for prevention of security failures |
| CC7.4 | Implementation of Incident-response Programme to identify and respond to Security Incidents |
| CC7.5 | Creation and execution of activities to recover from known Security-incidents |
CC8 Series – Change Management Controls
There is only one control in this series. It relates to significant changes in policies and procedures for updating infrastructure, software, data, and processes. The main aim of CC8 control is to establish an approval hierarchy to manage changes.
| Control Criteria | Objective |
|---|---|
| CC8.1 | Establishing a hierarchy of approvals for any changes to policies and procedures governing updating of infrastructure, data, software, and processes. |
CC9 Series – Risk Mitigation Controls
Risk Mitigation Controls concentrate on identification of risks and outlining of activities to mitigate those risks.
| Control Criteria | Objective |
|---|---|
| CC9.1 | Prescription and development of risk mitigation activities |
| CC9.2 | Assessment and management of risks associated with business partners and vendors |
Specific Criteria Controls
Specific Criteria Controls are for the optional TSCs, ‘Availability’, ‘Processing Integrity’, ‘Confidentiality’, and ‘Privacy’.
Controls to ensure ‘Availability’
| Control Criteria | Objective |
|---|---|
| A1.1 | Monitoring and evaluation of current processing capacity and the use of infrastructure, data, and software for the management and extension of capacity demand |
| A1.2 | Management and operation of software, environmental protections, data backup processes, and infrastructure for data recovery |
| A1.3 | Testing of recovery plan procedures |
Controls to maintain ‘Processing Integrity’
Processing Integrity Controls deal with situations when an organization is transacting on behalf of another organization. It may be your Startup’s client or a customer.
| Control Criteria | Objective |
|---|---|
| PI 1.1 | Communication of relevant information regarding data, products, and services. |
| PI 1.2 | Accuracy and completeness of information |
| PI 1.3 | Continuity of system processes relating to products, services, and reporting |
| PI 1.4 | Availability and delivery of outputs accurately, completely, and timely |
| PI 1.5 | Adherence to specifications relating to storing inputs, processing items, and outputs |
Controls for preserving ‘Confidentiality’
| Control Criteria | Objective |
|---|---|
| C1.1 | Identification and maintenance of confidential information |
| C1.2 | Disposal of confidential information |
Controls to maintain ‘Privacy’
There are 18 controls dedicated to maintaining privacy of information. These controls concentrate on:
- Defining, management, and implementation of Privacy Policies
- Accessibility to private information for reviewing and updating
- Use, retention, and disposal of personal information
- Notifying consumers regarding the Privacy Policy, and changes and updates
- Protection of personal information by restricting logical and physical access
- Availability of the choice and consent for the use of personal information
- Collection and disclosure of personal information only for purposes and to parties as mentioned in the Privacy Policy
- Quality of management procedures for maintaining privacy of personal information
Process for SOC 2 for Startups

Step 1
Assembling the SOC 2 Team and Starting a Culture
The first step towards compliance involves assigning personnel the responsibility of sailing through the process. Larger companies have elaborate Governance, Risk, and Compliance or GRC teams for this purpose. However, as a Startup you will need a smaller team. Your SOC 2 team should include:
- A Technical Lead to communicate with the auditor. This person will act as a bridge between the SOC 2 team and the auditor. CTO or a VP of Engineering can be ideal for this role.
- A Business Process Lead to manage the compliance and auditing tasks. This person will define the workflow, delegate responsibilities, and establish deadlines. A COO or HR Manager is ideal for this role.
- An Information Security Lead, who will be responsible for Security Process Documentation. You may appoint a Director of Security for this purpose or assign this role to a Senior Engineer.
In case you cannot identify the individuals for the above roles, you can choose another way. Start by forming multidisciplinary teams with SOC 2 volunteers and authors. The authors translate the business requirements into policies with the help of volunteers. After making a few policies in this manner, you will be able to identify the right individuals for the SOC 2 team roles.
After setting up the team, you will need to communicate the significance of SOC 2 to all the employees. It’s important to establish a culture of security to move smoothly towards compliance. Promoting a Cybersecurity Culture will keep everyone in your organization well-informed. Besides, it will be crucial for subsequent SOC 2 reports and in scaling-up.
Step 2
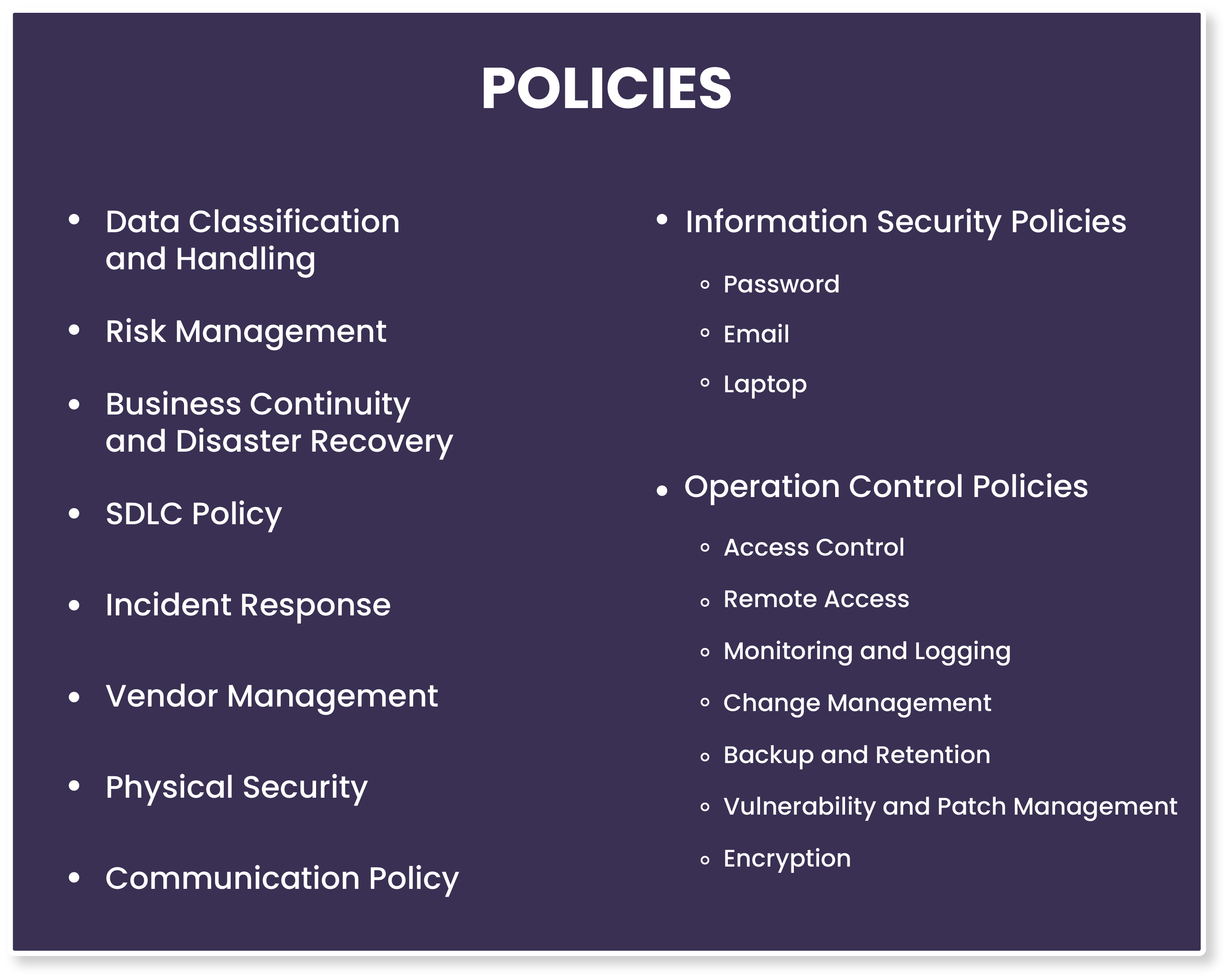
Setting up the Information Security Architecture
The InfoSec architecture will comprise systems, policies, and controls, besides the SOC 2 team. You may need to designate a person in each team to ensure adherence to data security rules.
Here’s a list of ‘Policies’ that will help you set up an InfoSec System for the categories and controls of your SOC 2 report. Please note that not all of them may apply in your case.
Step 3
Implementing SOC 2 Requirements
Put the data security processes, policies, and procedures into practice to check if they are working for you. Start by a Gap Analysis. Look for Gaps in the choice of Categories and Controls that you have identified.
After finalizing the scope of your SOC 2, check if you have required policies in place. Assign individuals within the organization to review the policies. Updates the policies and procedures. Don’t hesitate to employ an external reviewer!
Once you have plugged the gaps, you can move towards upgrading the Security Control Design within your organization. You may have to make slight adjustments to the business operations to meet the data security requirements.
Implementing SOC 2 requirements often requires upgrading hardware, software, and networks. Make sure that you make additional tools, services, licenses, and consultants available to your team to operationalize security controls.
Step 4
Evidence Collection and Documentation
Collect evidence showing that all the security controls within the organization are working as intended. The collected evidence has to be documented.
Some essential documentation includes:
- Management Assertions explains how the startup’s system fulfills the service commitments and meets the TSCs selected for the audit.
- System Descriptions show the components of the infrastructure that fall in the scope of the SOC 2 audit. Flowcharts and diagrams make up the Systems Descriptions.
- Control Matrix provides the details of the Controls, Criteria, and Categories.
The auditor refers to documentation and checks the claims regarding the operating security controls to create the SOC 2 report.
Please note that the auditor’s opinions make the SOC 2 Attestation Report, and they will be based on your documentation. Therefore, any lapse in collecting evidence and recording it will reflect in the SOC 2 audit report.
Step 5
Readiness Assessment and Remediation
Readiness Assessment is a rehearsal of the actual auditing performed by internal or external auditors. Its aim is to point out the gaps in security controls prior to the final audit.
You may choose to create a report from the mock audit, or simply concentrate on finding the deficiencies and remedial actions.
Step 6
Preparing for final SOC 2 Audit
Choose an auditing firm or a certified auditor to conduct the compliance audit for your company. Keep all the documentation ready for the auditor. Prepare your staff for the interviews that will include questions regarding business operations, security controls, and SLAs.
After receiving the Attestation Report, prepare for continuous monitoring and attaining the next SOC 2 report.
Following these six steps, you will be able to sail through your first SOC 2 process.
FAQs
Why should my Startup become SOC 2 compliant?
Your startup should become SOC 2 compliant to prove high standards of data security within your organization. SOC 2 compliant startups retain more customers and win mid-market and big-ticket clients. Prior SOC 2 compliance means smooth up-scaling and shorter sales cycles, and faster business growth. Compliant startups gain credibility amongst stakeholders.
When should I begin the process for SOC 2 compliance?
Growth stage is the best time for startups to invest in SOC 2, but a proactive approach is better. If an organization looking to do business with you demands an SOC 2 report, you won’t be able to present it at an instant. To be on the safer side, begin the SOC 2 process in the early stage of your startup. SOC 2 should be your priority task if you are planning to do business with enterprise clients.
How long does it take to get an SOC 2 report?
It may take one month to one year for the SOC 2 auditing process. It depends upon the complexity of the systems and processes, the size of your organization, the control categories opted, and the purpose of the audit. Type 1 audits take a few weeks, while Type 2 audits may require a whole year. The Monitoring Period for Type 2 audits may last up to 6 months.
What is the validity of the SOC 2 Attestation Report?
The SOC 2 Type 2 audit leads to an Attestation Report. SOC 2 Type 2 works on the principle of continuous evaluation since it assesses the controls and processes over a period. The Attestation Report can become irrelevant after a few months. Beginning the next compliance cycle soon after receiving the Attestation Report is the best way out.





